GREEN SYNTHESIS AND OPTOELECTRONIC CHARACTERIZATION OF SILVER NANOPARTICLE PREPARED USING AQUOUS HOUTTUNIA CORDATA LEAF EXTRACT AND ITS POTENTIAL APPLICATION AS ANTIBACTERIAL AGENT
Abstract
Author(s): Farhana Sultanaa* Jayanta Barmanb, Mousmi Saikiac
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its activity on bacterial pathogens have attracted a lot of attention due to possibility of their application in water treatment. The green synthesis metho d is a simple biological, environment-friendly and cost effective approach. In the present study, silver nanoparticles were rapidly synthesized using aqueous leaf extract of Houttuynia cordata as reducing and stabilizing agents and UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) and FTIR were used to monitor the quantitative formation of silver nanoparticles. The Transmission Electrone Microscopy (TEM) analysis reveals spherical shape of the synthesized nanoparticles and the size of Ag nanoparticles are in range 15 to 20 nm. The antibacterial potential of synthesized nanoparticles were investigated against cultures of gram negative bacteria Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia and gram positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. The result showed an enhanced antibacterial efficacy.

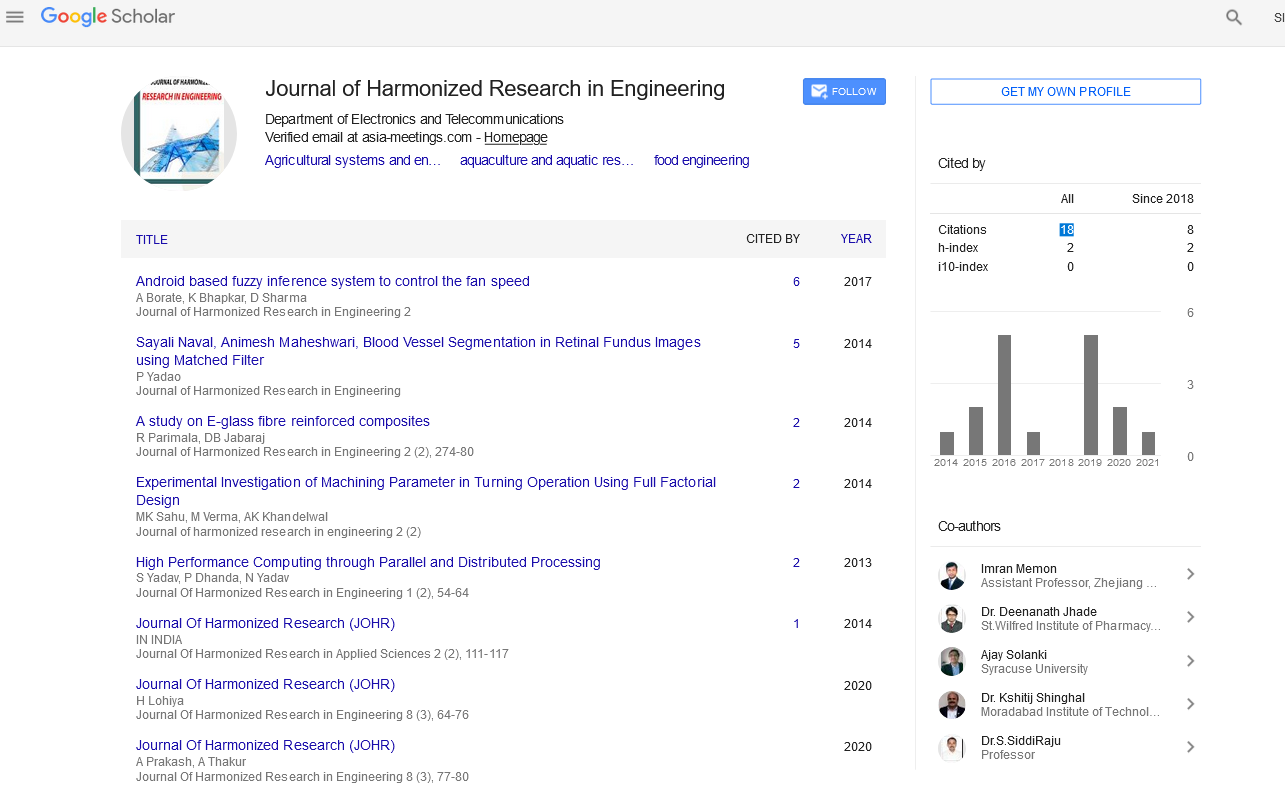
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 43
Journal of Harmonized Research in Engineering received 43 citations as per google scholar report