STANDARD GEOSPATIAL DATA MODEL FOR WATER AND WASTEWATER INFRASTRUCTURE RISK ASSESSMENT
Abstract
Author(s): Rahul Vemulapally, Sunil K. Sinha, and Stephen M.Welling
Geospatial pipeline attribute data is required for the enhanced risk assessment of buried water pipeline infrastructure. Toward this end, a GIS can provide water utilities a means for viewing, under standing, interpreting, and visualizing complex geographically referenced pipeline information to reveal data relationships, patterns, and trends. Yet, no standard data model exists for utilities to follow in order to enable advanced risk assessment modeling. The primary objectives of this research were to develop a standard GIS data model to conflate disparate datasets from differing utilities, and further demonstrate its usefulness through developing risk assessment applications using the standardized data from participating utilities and publicly available data, such as that from the USGS. Field mapping files were generated from the standard data model and demonstrated in a Google Earth application using a risk score for the pipeline, and further a web-based mapping application using ArcGIS Server Manager for publishing, querying and the visualization of aggregated data in a map-based browser application. The aggregation of standardized data and further use in mapping applications will help in providing timely access to asset management information and resources that will lead to enhanced risk modeling for drinking water and wastewater utilities.

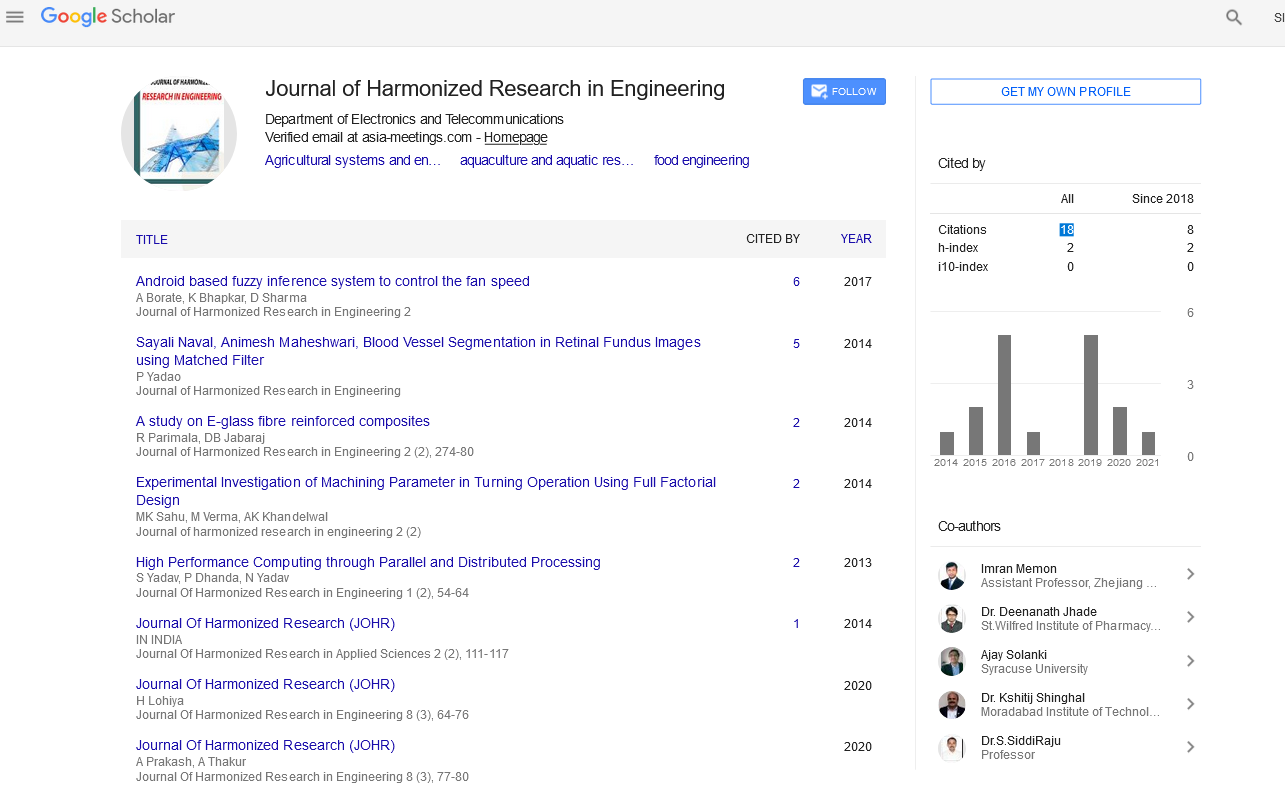
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 43
Journal of Harmonized Research in Engineering received 43 citations as per google scholar report